




| R- Value |
Batts or Blankets | Loose and Blown Fill | |||||
| Glass Fiber | Rock Wool | Glass Fiber |
Rock Wool |
Cellulose Fiber |
Vermiculite | Perlite | |
| R-11 | 3 1/2 in | 3 in. | 5 in. | 4 in. | 3 in. | 5 in. | 4 in. |
| R-13 | 3 5/8 | 3 1/2 | 6 | 4 1/2 | 3 1/2 | 6 | 5 |
| R-19 | 6-6 1/2 | 5 | 8 1/2 | 6 1/2 | 5 | 9 | 7 |
| R-22 | 7 | 6 | 10 | 7 1/2 | 6 | 10 1/2 | 8 |
| R-26 | 8 | 7 | 12 | 9 | 7 | 12 1/2 | 9 1/2 |
| R-30 | 8 | 7 | 12 | 9 | 9 | 12 1/2 | 9 1/2 |
| R-30 | 9 1/2 | 8 | 13 1/2 | 10 | 8 | 14 | 11 |
| R-33 | 10 1/2 | 9 | 15 | 11 | 9 | 15 1/2 | 12 |
| R-38 | 12 | 10 1/2 | 17 | 13 | 10 | 18 | 14 |
| Material | R-Value | |
| Per 1" Thickness | For Thickness Listed | |
| Polyurethane | 6.00 | |
| Expanded Polystyrene, molded | 4.00 | |
| Expanded Polystyrene, extruded | 5.00 | |
| Expanded Polystyrene, molded beads | 3.57 | |
| Polyisocyanurate | 7.20 | |
| Fiberboard 1/2" | 1.32 | |
| Fiberboard 3/4" | 2.10 | |
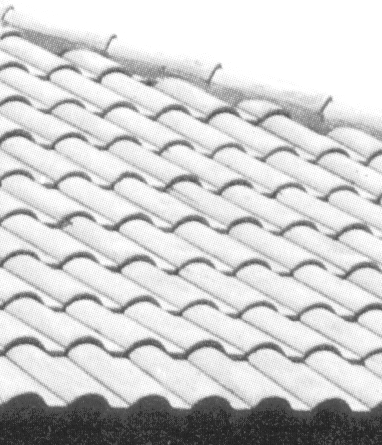
ANSWERS TO ACTIVITY 4:
| Type of Roof | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| 1. asphalt/fiberglass | -not expensive -easy to install -fairly long lasting -attractive |
-has little value in reducing heat gain |
| 2. metal roof | -not degraded by sun -has long life -adaptable to many building designs -lightweight, rigid -has variety in colors & textures -has positive slope for draining |
-could develop leaks if not properly installed -could be damaged by wind -not readily accepted in some subdivisions |
| 3. clay tile roof | -energy efficient -attractive -long lasting -fire resistant -well suited for hot, dry climate |
-very expensive -heavy -not suited for rainy climates |
Comments or questions to: TechAsmt@LA.GOV
Return to Carpentry Menu